What is the cause of the development of cervical cancer, what is HPV, how is it transmitted, what are the symptoms, how is it treated and how can it be prevented – Dr. Jasmina Veta Darkovski, specialist in gynecology and obstetrics, for fitnesdietplan24.com. com answers the most frequently asked questions on this topic.
Women’s health is an important topic that must be discussed more often and more openly, with the aim of education and getting to know our body, but also prevention of unwanted diseases, as well as their timely detection and treatment.
In addition to mandatory regular examinations with a gynecologist, it is important that you yourself are aware of the changes that occur in your body, which may cause problems that you must not ignore.
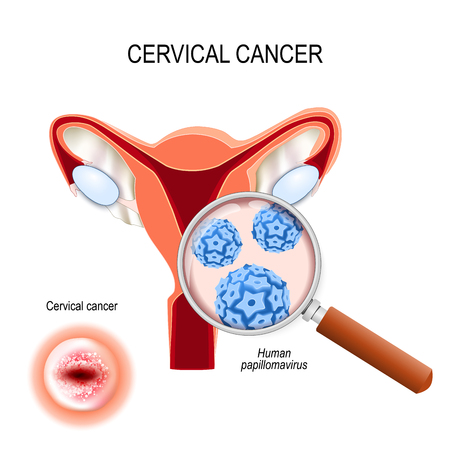
What is the reason for the development of cervical cancer?
The most common reason (more than 90%) for the development of premalignant and malignant disease of the cervix is infection with HPV (human papilloma virus).
Carcinoma of the cervix is the 3rd most common malignant disease of the female genital system worldwide.
What is HPV (human papilloma virus)?
A virus from the family of papillomaviruses.
There are two groups of HPV: low and high-risk group of viruses, which can cause benign and malignant diseases of the female genital system.
One of the benign skin diseases are warts (condylomas) caused by the low-risk group of HPV (40, 42, 43, 44, 54, 61, 72, 81).
High-risk HP-Viruses (16, 18, 31, 33, 35, 39, 45, 51, 52, 56, 58, 59) cause premalignant changes (changes before a malignant disease develops), so-called cervical dysplasia and malignant diseases (carcinoma) if a dysplasia is not detected in time.

How is the infection transmitted?
The infection is transmitted exclusively through sexual contact. Mostly the first contact ie. infection is acquired at the age of 20-25 years.
What happens if there is a high-risk HPV infection?
In immunocompetent persons (persons with a continuously good immune system), the infection will be cured by itself, ie. will withdraw and will not leave any consequences.
In people with a permanently or temporarily weakened immune system, it is possible to develop a disorder in the maturation of the epithelial cells of the cervix and the development of dysplasia, and in a more advanced stage, the development of malignant cell change.
What are the symptoms?
Most often, premalignant and malignant diseases due to infection with a high-risk group of HPV are asymptomatic (without symptoms).
Sometimes they may call:
- contact bleeding after intercourse,
- change in vaginal discharge (increased secretion, change in color and smell),
- frequent itching,
- baking or
- feeling of dryness in the part of the external genitalia, if there is a disease of the labia majora and minora of the vulva, vagina and anus.
How can it be detected?
Regular gynecological examination and cytological smear (PAP-Smear) and determination of human papilloma virus in the smear.
If the smear is suspicious, a referral to a gynecologist subspecialist and an examination with a colposcope will follow.
Colposcopy is an examination with a microscope, with which, by enlarging the opening of the uterus, suspicious regions can be determined and a biopsy (taking a tissue sample) can be made from them.
The tissue will be sent for histological examination, which will clarify the diagnosis and determine the stage of the disease.
Who performs the tests?
Family gynecologist: regular gynecological examination and Pap smear and referral to a subspecialist gynecologist for malignant diseases.
Cytologist: examination of smears under a microscope. This describes the appearance and maturity stage of the cells, as well as their maturational changes.
Pathologist: tissue examination, if a cervical biopsy was performed. In doing so, the stage of the change/disease of the tissue is determined.
What next?
If only a premalignant disease of the cervix is diagnosed, it can be completely removed with a low-risk surgical intervention. The operative intervention is called conization.
Conization refers to the removal of a small part of the cervix in the form of a cone. If the disease is detected at a more advanced stage, there is little possibility of completely removing the change.
Treatment is carried out using radiation therapy called radiotherapy and chemotherapy. The disease detected in a more advanced stage has a poor prognosis, ie. the possibility of a complete cure is minimal.
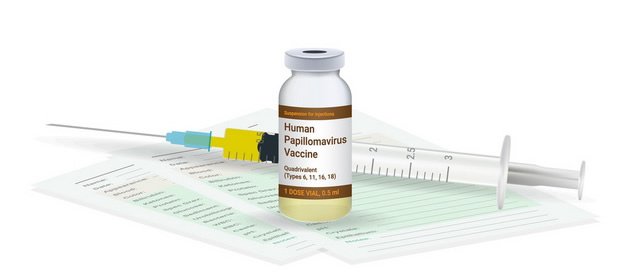
How can malignant disease of the cervix be prevented?
There has been a vaccine against HPV-Infection since ten years ago. The vaccine is intended for both the female and male population from 9 to 17 years of age.
The ideal time for vaccination is before starting sexual activity. In high-risk patients and after surgery, it is possible to carry out the vaccination later.
What is the purpose of timely detection of premalignant conditions of the cervix?
Short-term as well as long-term reduction in incidence and mortality (death rate from a particular disease).
At the same time, improving the quality of life of sick patients.
The text was prepared by Dr. Jasmina Veta Darkovski, a specialist in gynecology and obstetrics, who currently heads the special clinic for premalignant diseases of the female genital system (vulva, vagina and cervix), in Meissen, Germany.
Dr. Jasmina Veta Darkovski will write educational texts on various topics related to women’s health for fitnesdietplan24.com